Single Blood Test Screens for Eight Cancer Types
Provides unique new framework for early detection of the most common cancers
Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center researchers developed a single blood test that screens for eight common cancer types and helps identify the location of the cancer.
The test, called CancerSEEK, is a unique noninvasive, multianalyte test that simultaneously evaluates levels of eight cancer proteins and the presence of cancer gene mutations from circulating DNA in the blood. The test is aimed at screening for eight common cancer types that account for more than 60 percent of cancer deaths in the U.S. Five of the cancers covered by the test currently have no screening test.
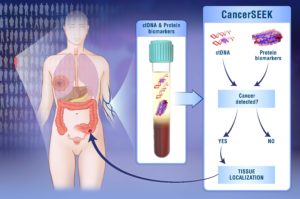
“The use of a combination of selected biomarkers for early detection has the potential to change the way we screen for cancer, and it is based on the same rationale for using combinations of drugs to treat cancers,” says Nickolas Papadopoulos, Ph.D., senior author and professor of oncology and pathology.
The findings were published online by Science on Jan. 18, 2018.
“Circulating tumor DNA mutations can be highly specific markers for cancer. To capitalize on this inherent specificity, we sought to develop a small yet robust panel that could detect at least one mutation in the vast majority of cancers,” says Joshua Cohen, an M.D.-Ph.D. student at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and the paper’s first author. “In fact, keeping the mutation panel small is essential to minimize false-positive results and keep such screening tests affordable.”
The investigators initially explored several hundred genes and 40 protein markers, whittling the number down to segments of 16 genes and eight proteins. They point out that this molecular test is solely aimed at cancer screening and, therefore, is different from other molecular tests, which rely on analyzing large numbers of cancer-driving genes to identify therapeutically actionable targets.
In this study, the test had greater than 99 percent specificity for cancer. “Very high specificity was essential because false-positive results can subject patients to unnecessary invasive follow-up tests and procedures to confirm the presence of cancer,” says Kenneth Kinzler, Ph.D., professor of oncology and co-director of the Ludwig Center. The test was used on 812 healthy controls and produced only seven false-positive results.
The test was evaluated on 1,005 patients with nonmetastatic, stages I to III cancers of the ovary, liver, stomach, pancreas, esophagus, colorectum, lung or breast. The median overall sensitivity, or the ability to find cancer, was 70 percent and ranged from a high of 98 percent for ovarian cancer to a low of 33 percent for breast cancer. For the five cancers that have no screening tests—ovarian, liver, stomach, pancreatic and esophageal cancers—sensitivity ranged from 69 percent to 98 percent.
“A novelty of our classification method is that it combines the probability of observing various DNA mutations together with the levels of several proteins in order to make the final call,” says Cristian Tomasetti, Ph.D., associate professor of oncology and biostatistics, who developed the algorithm. “Another new aspect of our approach is that it uses machine learning to enable the test to accurately determine the location of a tumor down to a small number of anatomic sites in 83 percent of patients.”
Read the rest of the article here https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/news/media/releases/single_blood_test_screens_for_eight_cancer_types
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Clinical Reference Laboratory Services Market to Witness Excellent Long-Term Growth Outlook
HTF MI published a new industry research that focuses on Clinical Reference Laboratory Services market and delivers in-depth market analysis and future prospects of Global Clinical Reference Laboratory Services market. The study covers significant data which makes the research document a handy resource for managers, analysts, industry experts and other key people get ready-to-access and self-analyzed study along with graphs and tables to help understand market trends, drivers and market challenges. The study is segmented by Application/ end users [Clinical Chemistry, Clinical Blood, Fluidology, Clinical Immunology, Clinical Microbiology & Clinical Blood Transfusion], products type [Compound Screening, Pharmacology & Toxicology] and various important geographies like United States, EU, Japan, China, India & Southeast Asia].
Get Access to sample pages @ https://www.htfmarketreport.com/sample-report/867114-global-clinical-reference-laboratory-services-market-2
The research covers the current market size of the Global Clinical Reference Laboratory Services market and its growth rates based on 5 year history data along with company profile of key players/manufacturers. The in-depth information by segments of Clinical Reference Laboratory Services market helps monitor future profitability & to make critical decisions for growth. The information on trends and developments, focuses on markets and materials, capacities, technologies, CAPEX cycle and the changing structure of the Global Clinical Reference Laboratory Services Market.
The study provides company profiling, product picture and specifications, sales, market share and contact information of key manufacturers of Global Clinical Reference Laboratory Services Market, some of them listed here are SCTC, Kingmed, Adicon, DIAN DIAGNOSTICS, Kindstar, DAAN GENE, Surexam, Amoydx, KeyTest, JOY ORIENT & Ipe-bio. The market is growing at a very rapid pace and with rise in technological innovation, competition and M&A activities in the industry many local and regional vendors are offering specific application products for varied end-users. The new manufacturer entrants in the market are finding it hard to compete with the international vendors based on quality, reliability, and innovations in technology.
Global Clinical Reference Laboratory Services (Thousands Units) and Revenue (Million USD) Market Split by Product Type such as Compound Screening, Pharmacology & Toxicology. Further the research study is segmented by Application such as Clinical Chemistry, Clinical Blood, Fluidology, Clinical Immunology, Clinical Microbiology & Clinical Blood Transfusion with historical and projected market share and compounded annual growth rate.
Geographically, this report is segmented into several key Regions, with production, consumption, revenue (million USD), and market share and growth rate of Clinical Reference Laboratory Services in these regions, from 2012 to 2022 (forecast), covering United States, EU, Japan, China, India & Southeast Asia and its Share (%) and CAGR for the forecasted period 2017 to 2022.
Read Detailed Index of full Research Study at @ https://www.htfmarketreport.com/reports/867114-global-clinical-reference-laboratory-services-market-2
From Many One: A Case Study on Standardizing Point of Care Testing Instrumentation
Author: Brenda Suh-Lailam, PhD, DABCC, FACB Source: Clinical Laboratory News
Point-of-care testing (POCT) goes a long way toward helping institutions improve patient care by returning fast and reliable results near patients, thereby enabling prompt clinical interventions. POCT’s vital role in patient management makes it popular across clinical settings but often with different device types for the same test. Our institution is no exception to this POCT device creep, as at one point we had more than four types of blood gas analyzers, three table tops and one hand-held. Realizing that this confounded many of our quality and efficiency aims, we undertook a deliberate and durable process to standardize these instruments, using the general process outlined in Figure 1.
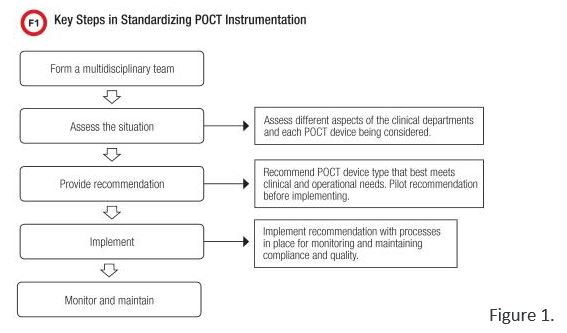
Read the Full Article here: https://www.aacc.org/publications/cln/articles/2017/november/from-many-one-a-case-study-on-standardizing-point-of-care-testing-instrumentation
Point-of-Care Testing Brings Efficiencies to Primary Care Practices
Source: Clinical Laboratory News
Implementing point-of-care testing (POCT) in a general internal medicine practice led to a statistically significant 99% reduction in letters to patients and demonstrated a net financial benefit to the practice of $11.90-$14.74 per patient visit (Clin Chim Acta 2017; doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2017.08.019). The findings build on the authors’ prior research involving POCT implementation in an academic institution-based primary care office and confirm that POCT improves primary care practice efficiency to varying degrees.
Read the Full Article: https://www.aacc.org/publications/cln/articles/2017/october/point-of-care-testing-brings-efficiencies-to-primary-care-practices
Close Up on the Opioid Crisis
Labs have a key role in advising physicians, providing optimal testing
Author: Brittany Moya del Pino Source: Clinical Laboratory News
The shadow of prescription painkiller abuse now looms more ominously than ever before. As starkly detailed in a December 2016 Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, opioids in 2015 accounted for more than two-thirds of all drug overdose deaths in the United States, 15.6% more than the previous year, and drug overdose deaths nearly tripled between 1999 and 2014. Yet opioids remain a mainstay of pain management, upping the stakes for monitoring prescription compliance and detecting abuse.
Read the Full Article: https://www.aacc.org/publications/cln/articles/2017/may/close-up-on-the-opioid-crisis-labs-have-a-key-role-in-advising-physicians-providing-optimal-testing
Recommended Reading:
Tietz Textbook of Clinical Chemistry and Molecular Diagnostics, 6th Edition
The Tietz Textbook of Clinical Chemistry and Molecular Diagnostics, 6th Edition provides the most current and authoritative guidance on selecting, performing, and evaluating the results of new and established laboratory tests.
Learn more about it here: https://www.aacc.org/store/books/11600/tietz-textbook-of-clinical-chemistry-and-molecular-diagnostics-6th-edition
Links of Interest: